Middleware In ASP.NET Core
Understanding Middleware in .NET Core
– Middleware is a piece of code in an application pipeline used to handle requests and responses.
– We may have a middleware component to authenticate a user, another piece of middleware to handle errors, and another middleware to serve static files such as JavaScript files, CSS files, images, etc.
– Middleware can be built-in as part of the .NET Core framework, added via NuGet packages, or can be custom middleware.
– These middleware components are configured as part of the application startup class in the configure method.
– Configure methods set up a request processing pipeline for an ASP.NET Core application. It consists of a sequence of request delegates called one after the other.
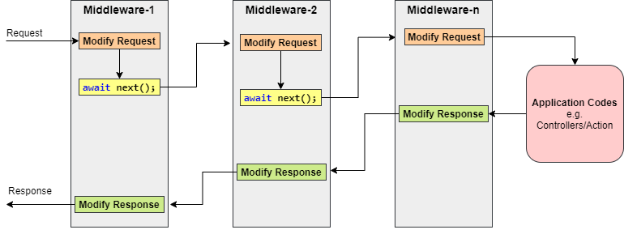
– Middleware components can decide not to call the next piece of middleware in the pipeline. This is called short-circuiting or terminating the request pipeline.
– Short-circuiting is often desirable because it avoids unnecessary work.
– Middleware components are executed in the order they are added to the pipeline, and care should be taken to add the middleware in the right order; otherwise, the application may not function as expected.
– This ordering is critical for security, performance, and functionality.
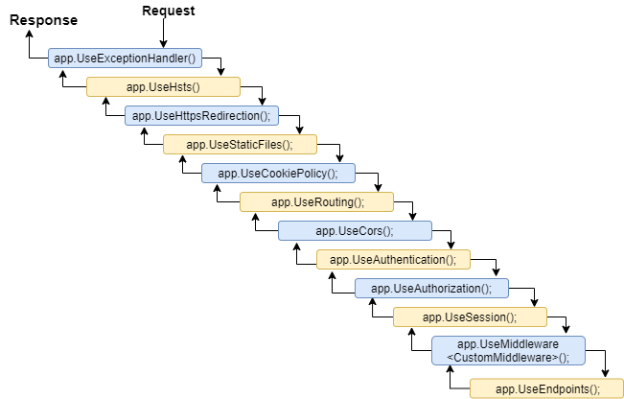
– Some middleware components may expose Run[Middleware] methods that run at the end of the pipeline.
Middleware Components
· Management console: Provides an overview of the middleware’s activities and configurations.
· Client interface.
· Internal interface.
· Platform interface.
· Contract manager.
· Session manager.
· Database manager.
· Runtime monitor.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!