Snowflake Architecture
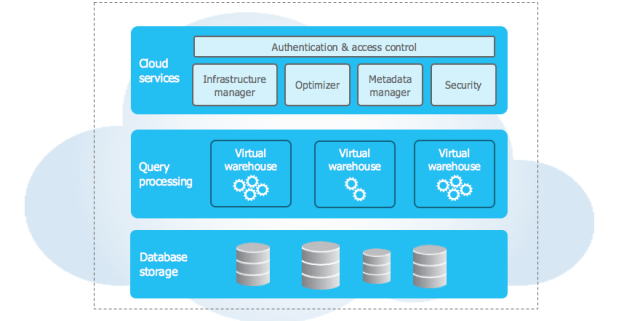
Snowflake’s follow hybrid architecture and it is a combination of traditional shared-disk and shared-nothing database architectures. Similar to shared-disk architectures, Snowflake uses a central data repository for persisted data that is accessible from all compute nodes in the platform. But similar to shared-nothing architectures, Snowflake processes queries using MPP (massively parallel processing) compute clusters where each node in the cluster stores a portion of the entire data set locally. This approach offers the data management simplicity of a shared-disk architecture, but with the performance and scale-out benefits of a shared-nothing architecture. Physically separated each layer but logically integrated, each layer can scale up and down independently, enabling Snowflake to be more elastic and responsive. Snowflake architecture allows data engineers, data analysts, and data scientists to maximize productivity without the performance, scale, or concurrency limitations of other solutions.
Snowflake has a multi-cluster, shared-data architecture that consists of three key layers, namely:
· Database Storage layer
· Query Processing layer
· Cloud Services layer

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!