ASP.NET Core – Environment Variable
· ASP.NET Core uses an environment variable called ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT to indicate the runtime environment.
· The value of this variable can be anything as per your need but typically it can be Development, Staging, or Production.
· The value is case insensitive in Windows and Mac OS but it is case sensitive on Linux.
· In Visual Studio, we can set ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT in the debug tab of project properties.
· Open project properties by right clicking on the project in the solution explorer and select Properties.
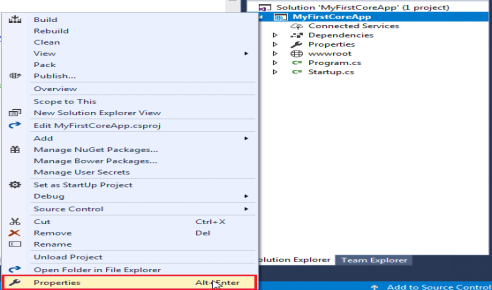
· This will open properties page. Click on Debug tab and you will see Environment Variables as shown below.
· You may change the value as per your need. This value will be saved in the launchSettings.json file as shown below.
· You may also change the environment variable directly in launchSettings.json.
Access Environment Variable at Runtime
· We can get the value of an environment variable in our code to execute some additional code based on its value.
· The IHostingEnvironment service includes EnvironmentName property which contains the value of ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT variable.
· ASP.NET Core also includes extension methods to check the environment such as IsDevelopment(), IsStating(), IsEnvironment() and IsProduction().
· The IHostingEnvironment service is provided by ASP.NET hosting layer and can be used anywhere in your application via Dependency Injection.
· Given below example shows how we can check the environment variable in the Configure method of Startup class.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsEnvironment(“Development”))
{
// code to be executed in development environment
}
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
// code to be executed in development environment
}
if (env.IsStaging())
{
// code to be executed in staging environment
}
if (env.IsProduction())
{
// code to be executed in production environment
}
}

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!